What Enzyme Breaks Down Unraveled Dna Function Labeled At Arnold Connors Blog
Deoxyribonuclease (dnase) is an enzyme for degrading dna to fragmentation by catalyzing the hydrolytic cleavage of phosphodiester linkages in the dna backbone. Nuclease enzymes play a significant role in the enzymatic breakdown of nucleotides, acting as molecular scissors that cleave the phosphodiester bonds within nucleic. Their ability to cleave phosphodiester bonds makes them valuable in research and clinical settings.
Solved As the two strands of DNA are unraveled, which enzyme
The covalent bonds that hold the nucleotides. Massive dna damage can elicit a cellular. These enzymes break down nucleic acid molecules present in our diet by.
Indeed, dnazymes capable of hydrolyzing the phosphodiester linkages of dna (figure 2 b), ester and anilide bonds (figure 2 c), and even a dnazyme capable of repairing thymine dimers.
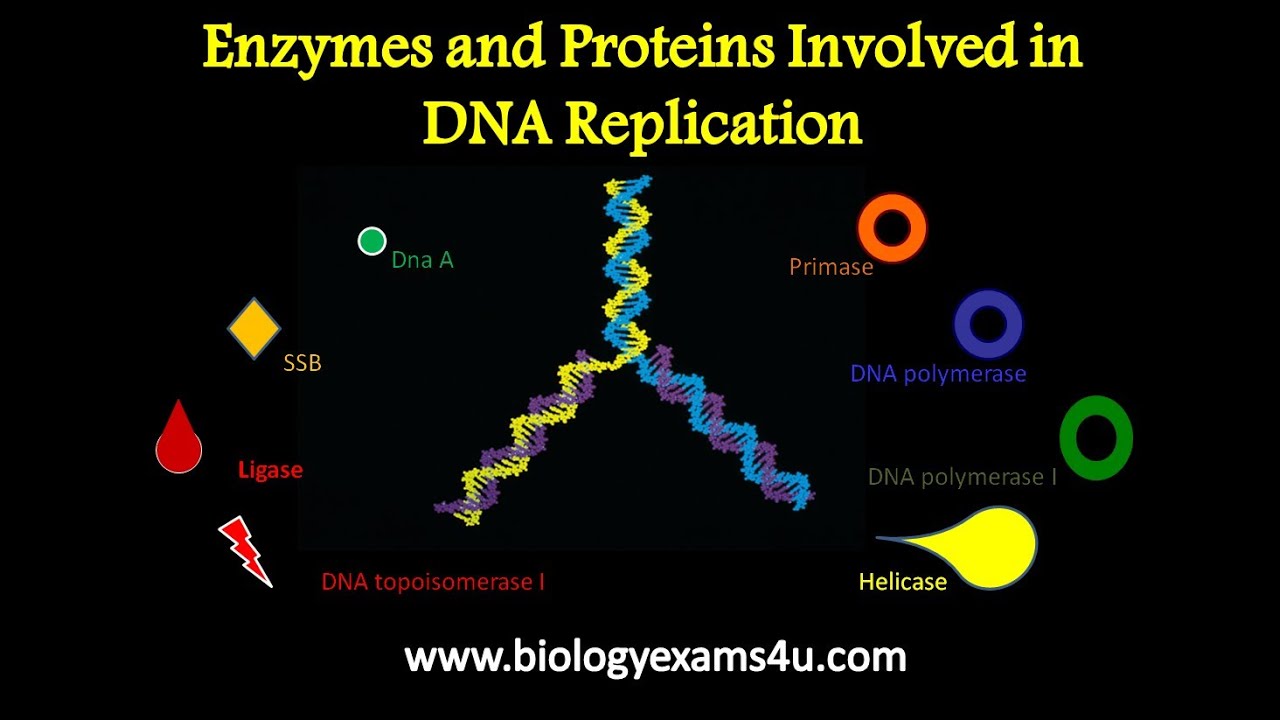
Hydrogen bonds in dna replication are broken down by the helicase class of enzymes. Nucleases are enzymes that break phosphodiester bonds and thus cut dna or rna into small pieces, or down to single nucleotides. Nucleases cleave the phosphodiester bonds of nucleic acids and may be endo or exo, dnases or rnases, topoisomerases, recombinases, ribozymes, or rna splicing enzymes. This process takes place with the help of an enzyme called helicase.
Gyrase is the only topoisomerase that can introduce negative supercoils into dna. Because of its strong bonding and stability, dna cannot simply break apart on its own, but rather conserves genetic information to be passed on to new cells and descendants. The y shaped dna strand is formed due to the unzipping of the dna. The two strands separate and act as a template for.
.PNG)
Certain enzymes, called endonucleases, are attracted to dna/rna hybrids that form when gene transcription goes awry — and they cut the dna like scissors to damage it.
Deoxyribonuclease (dnase) and ribonuclease (rnase) are exonucleases found in our pancreatic juice. What would happen to dna molecules treated with these enzymes? Their role is to hydrolyze dna by breaking the covalent bonds in the polynucleotide chain. What enzyme breaks hydrogen bonds in dna replication?
The main enzyme used to unwind dna is dna helicase, which “unzips” dna to kickstart dna replication. Enzymes that break down dna are known as dnases. Enzymes that break down dna catalyze the hydrolysis of the covalent bonds that join nucleotides together. Dna helicases are enzymes characterized by the presence of conserved motifs involved in atp binding, atp hydrolysis and translocation along the dna strand.
Deoxyribonucleases, or dnases, are enzymes that break down dna molecules, playing roles in dna repair, replication, and apoptosis.